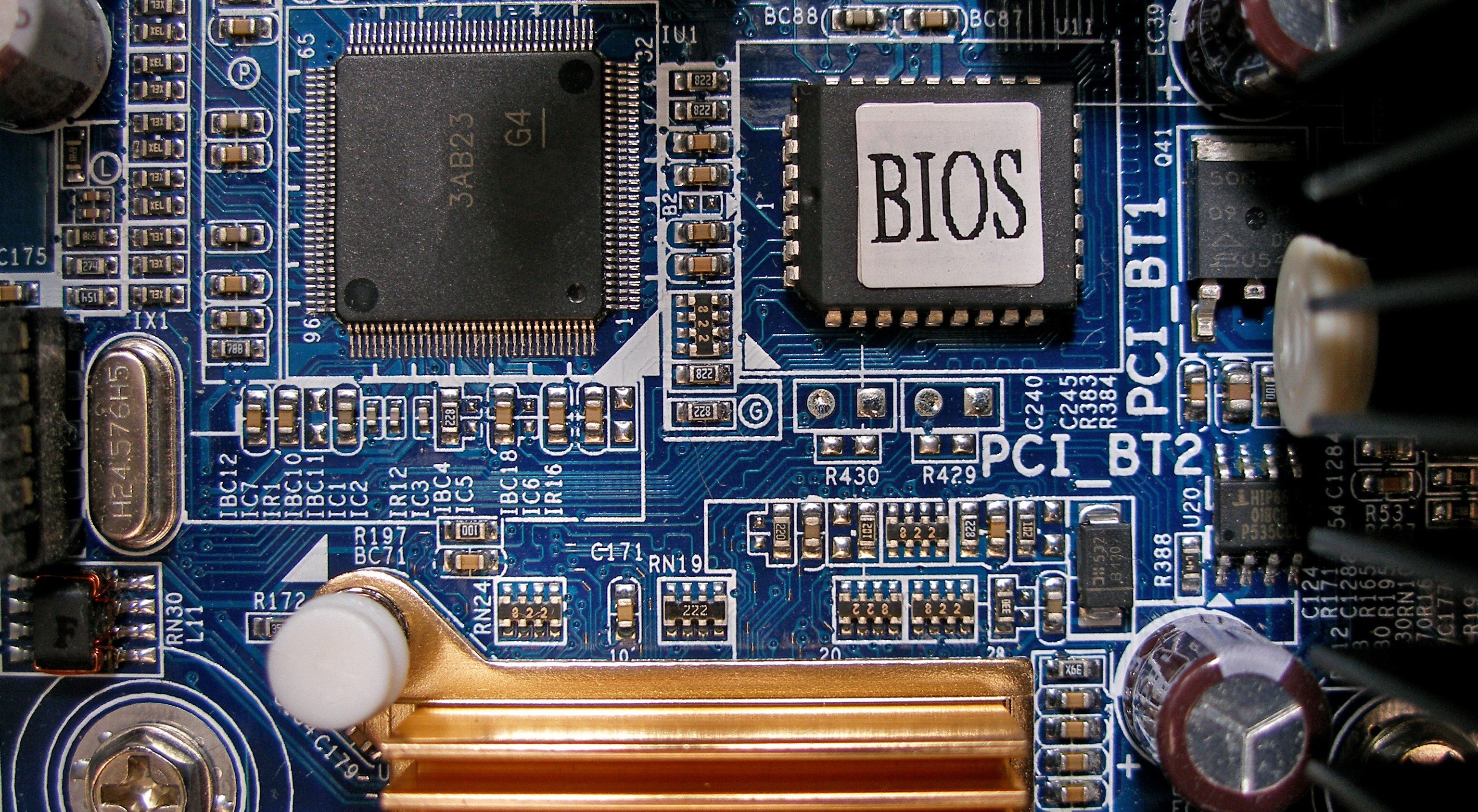
Right after a computer is turned on, it is important to make sure that there are no issues with hardware that could potentially compromise the computer’s functionality.
In this blog, you’ll learn more about what BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) is and why it’s an integral part of the booting process to ensure effective operation.
What is BIOS?
BIOS, or Basic Input/Output System, is software stored on a small memory chip (firmware) on the motherboard, and it is the very first software to run after a computer starts.
The BIOS instructs the computer on how to perform basic functions such as booting and keyboard control. The BIOS is also used to identify and configure the hardware in a computer such as the hard drive, floppy disk, optical drive, CPU, memory, and related equipment.
Finally, it manages data flow between the computer’s operating system (OS) and attached devices.
BIOS firmware is non-volatile, meaning that its settings are saved and recoverable even after power has been removed from the device.
Why is BIOS important?
In essence, the BIOS identifies, configures, tests, and connects computer hardware to the OS after a computer is turned on. (This is called the boot process.)
The BIOS is responsible for POST, or Power-on Self-Test, the initial set of diagnostic tests performed by the computer right after it is powered on, with the intent to check for any hardware related issues.
POST is the first step of the boot sequence, and it is always going to run regardless of whether you’ve just restarted your computer or you’re turning it on for the first time in days.
POST does not rely on any specific operating system. In fact, there does not even need to be an OS installed on a hard drive for it to run. This is because POST is handled by the BIOS, not any installed software. If an OS is installed, POST runs before it has a chance to start up.
POST checks that basic system devices are present and working properly, like the keyboard and other peripheral devices, and other hardware elements like the processors, storage devices, and memory.
The computer will continue to boot after POST, but only if POST is successful. If POST finds an issue, you will get an error of some kind, and hopefully, it is clear enough for you to jump-start the troubleshooting process.

Source: hpcwire.com. BIOS is responsible for POST, Power-on Self-Test, the initial set of diagnostic tests performed by the computer right after it is powered on, with the intent to check for any hardware related issues.
How to access BIOS
The BIOS is accessed and configured through the BIOS Setup Utility. The BIOS Setup Utility is, in essence, the BIOS itself. All available options in BIOS are configurable through the BIOS Setup Utility.
Unlike an operating system, BIOS comes installed from the moment a system is manufactured.
The BIOS Setup Utility can be accessed in various ways depending on the computer or motherboard make and model.
What contains BIOS?
All modern computer motherboards contain BIOS software.
BIOS access and configuration are independent of any operating system because the BIOS is part of the motherboard hardware.
Irrespective of whether or not an operating system is installed, the BIOS functions outside of the operating system environment.
BIOS Manufacturers
Some of the most popular BIOS vendors are:
How to use BIOS
BIOS supports several hardware configuration options the can be changed through the setup utility. Saving these changes and restarting the computer applies the changes to the BIOS and alters the way BIOS instructs the hardware to function.
Here are some common things you can do in most BIOS systems:
- Change the Boot Order
- Load BIOS Setup Defaults
- Flash (Update) BIOS
- Remove a BIOS Password
- Create a BIOS Password
- Change the Date and Time
- Change Floppy Drive Settings
- Change Hard Drive Settings
- Change CD/DVD/BD Drive Settings
- View Amount of Memory Installed
- Change the Boot Up NumLock Status
- Enable or Disable the Computer Logo
- Enable or Disable the Quick Power On Self Test (POST)
- Enable or Disable the CPU Internal Cache
- Enable or Disable the Caching of BIOS
- Change CPU Settings
- Change Memory Settings
- Change System Voltages
- Enable or Disable RAID
- Enable or Disable Onboard USB
- Enable or Disable Onboard IEEE1394
- Enable or Disable Onboard Audio
- Enable or Disable Onboard Floppy Controller
- Enable or Disable Onboard Serial/Parallel Ports
- Enable or Disable ACPI
- Change the ACPI Suspend Type
- Change the Power Button Function
- Change Power-on Settings
- Change Which Display is Initialized First on Multi-Display Setups
- Reset Extended System Configuration Data (ESCD)
- Enable or Disable BIOS Control of System Resources
- Change Fan Speed Settings
- View CPU and System Temperatures
- View Fan Speeds
- View System Voltages
BIOS Security
Cyberattacks have become increasingly sophisticated, and traditional safeguards are proving to be ineffective in the face of these advanced attacks.
Without BIOS security, hackers can easily access and manipulate a computer’s information, gaining control over your system up to the highest level.
These data breaches are often very difficult to detect, even when using high-level scanning and other protective measures.
There are three primary methods used to protect your BIOS: passwords, full-disk encryption, and trusted platform modules.
Read more on how to secure your BIOS here.
BIOS and Trenton Systems
At Trenton, we design, manufacture, assemble, test, and support all of our systems right here in the USA.
Our expert team of engineers spends countless hours customizing the BIOS in-house to deliver an unprecedented level of system flexibility and customization capabilities based on the customer’s exact configuration.
We control the BIOS firmware and source code to lock down and disable common exploitation points for independent and state sponsored hackers.
With advanced, multi-layer cybersecurity technologies, we protect all system parts and components, including the BIOS, against unauthorized access, guarding sensitive and classified information at the highest level.
A secure, functioning BIOS equips a computer with right tools for immediate detection of hardware issues that post a risk to its operational integrity, ensuring optimal performance at the edge, anywhere, anytime.





 Users Today : 2
Users Today : 2 Users Yesterday : 4
Users Yesterday : 4 Users Last 7 days : 33
Users Last 7 days : 33 Users Last 30 days : 158
Users Last 30 days : 158 Users This Month : 104
Users This Month : 104 Users This Year : 1840
Users This Year : 1840 Total Users : 4452
Total Users : 4452 Views Today : 9
Views Today : 9 Views Yesterday : 14
Views Yesterday : 14 Views Last 7 days : 127
Views Last 7 days : 127 Views Last 30 days : 461
Views Last 30 days : 461 Views This Month : 338
Views This Month : 338 Views This Year : 4453
Views This Year : 4453 Total views : 11840
Total views : 11840 Who's Online : 0
Who's Online : 0